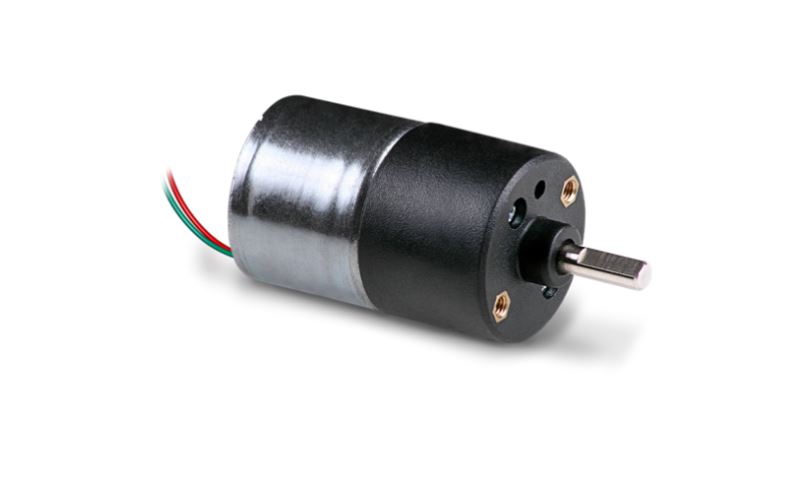
Product Description
|
Model NO |
28HS30 | Type | Electromechanical |
|
Certification |
CCC,ISO90O1,Ce | Brand | chensite |
|
efficiency |
high | size | NEMA 11 |
|
Length |
34mm | Weight | 120g |
|
Transport Package |
carton | Specification | 110g/140g/180g |
|
Trademark |
chensite | Origin | china |
|
HS Code |
8501310000 | Production Capacity | 50000/year |
Detailed Photos
The stepper geared motor driver controls the stepper geared motor winding through the internal logic circuit according to the external control pulses and direction signals, energising the stepper geared motor forwards or backwards for a certain period of time, so that the geared motor rotates or locks forwards/backwards. Take a 1.8 degree two-phase stepping geared motor as an example: when the two-phase winding is energised and excited, the output shaft of the geared motor will be stationary and locked in position. The maximum torque to lock the geared motor at rated current is the holding torque. If the current in 1 phase of the winding changes direction, the geared motor will rotate 1 step (1.8 degrees) in the given direction. Similarly, if the current in the other winding changes direction, the gearmotor will rotate 1 step (1.8 degrees) in the opposite direction to the former. When the current through the coil windings changes direction in sequence of excitation, the gearmotor will rotate continuously in the established direction with a very high degree of operating accuracy.1.8 degree two-phase stepper gearmotor rotates 200 steps per cycle.
Products Application
Factory Shows
Chensite is a leading manufacturer with advanced technology and innovative management mode. Hetaispecializes in producing servo motors,Dc Motors,hybrid stepping motors,drivers and so on.
Chensite dedicates to professional electrical integration and automation strategies for customers. The products are almost applied in obots, packing machinery, textile machinery,medical instruments, printing machinery, intelligent logistics equipment Chensite also sends its products to USA, Europe,Southeast Asia and all-around China.
Certifications
FAQ
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Printing Equipment |
|---|---|
| Speed: | High Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Four-Phase |
| Excitation Mode: | PM-Permanent Magnet |
| Number of Poles: | 8 |
| Operate Mode: | Three-Phase Six-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 19.9/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

How is the efficiency of a gear motor measured, and what factors can affect it?
The efficiency of a gear motor is a measure of how effectively it converts electrical input power into mechanical output power. It indicates the motor’s ability to minimize losses and maximize its energy conversion efficiency. The efficiency of a gear motor is typically measured using specific methods, and several factors can influence it. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Measuring Efficiency:
The efficiency of a gear motor is commonly measured by comparing the mechanical output power (Pout) to the electrical input power (Pin). The formula to calculate efficiency is:
Efficiency = (Pout / Pin) * 100%
The mechanical output power can be determined by measuring the torque (T) produced by the motor and the rotational speed (ω) at which it operates. The formula for mechanical power is:
Pout = T * ω
The electrical input power can be measured by monitoring the current (I) and voltage (V) supplied to the motor. The formula for electrical power is:
Pin = V * I
By substituting these values into the efficiency formula, the efficiency of the gear motor can be calculated as a percentage.
Factors Affecting Efficiency:
Several factors can influence the efficiency of a gear motor. Here are some notable factors:
- Friction and Mechanical Losses: Friction between moving parts, such as gears and bearings, can result in mechanical losses and reduce the overall efficiency of the gear motor. Minimizing friction through proper lubrication, high-quality components, and efficient design can help improve efficiency.
- Gearing Efficiency: The design and quality of the gears used in the gear motor can impact its efficiency. Gear trains can introduce mechanical losses due to gear meshing, misalignment, or backlash. Using well-designed gears with proper tooth profiles and minimizing gear train losses can improve efficiency.
- Motor Type and Construction: Different types of motors (e.g., brushed DC, brushless DC, AC induction) have varying efficiency characteristics. Motor construction, such as the quality of magnetic materials, winding resistance, and rotor design, can also affect efficiency. Choosing motors with higher efficiency ratings can improve overall gear motor efficiency.
- Electrical Losses: Electrical losses, such as resistive losses in motor windings or in the motor drive circuitry, can reduce efficiency. Minimizing resistance, optimizing motor drive electronics, and using efficient control algorithms can help mitigate electrical losses.
- Load Conditions: The operating conditions and load characteristics placed on the gear motor can impact its efficiency. Heavy loads, high speeds, or frequent acceleration and deceleration can increase losses and reduce efficiency. Matching the gear motor’s specifications to the application requirements and optimizing load conditions can improve efficiency.
- Temperature: Elevated temperatures can significantly affect the efficiency of a gear motor. Excessive heat can increase resistive losses, reduce lubrication effectiveness, and affect the magnetic properties of motor components. Proper cooling and thermal management techniques are essential to maintain optimal efficiency.
By considering these factors and implementing measures to minimize losses and optimize performance, the efficiency of a gear motor can be enhanced. Manufacturers often provide efficiency specifications for gear motors, allowing users to select motors that best meet their efficiency requirements for specific applications.

What are some common challenges or issues associated with gear motors, and how can they be addressed?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, can face certain challenges or issues that may affect their performance, reliability, or longevity. However, many of these challenges can be addressed through proper design, maintenance, and operational practices. Here are some common challenges associated with gear motors and potential solutions:
1. Gear Wear and Failure:
Over time, gears in a gear motor can experience wear, resulting in decreased performance or even failure. The following measures can address this challenge:
- Proper Lubrication: Regular lubrication with the appropriate lubricant can minimize friction and wear between gear teeth. It is essential to follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication intervals and use high-quality lubricants suitable for the specific gear motor.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Routine maintenance and periodic inspections can help identify early signs of gear wear or damage. Timely replacement of worn gears or components can prevent further damage and ensure the gear motor’s optimal performance.
- Material Selection: Choosing gears made from durable and wear-resistant materials, such as hardened steel or specialized alloys, can increase their lifespan and resistance to wear.
2. Backlash and Inaccuracy:
Backlash, as discussed earlier, can introduce inaccuracies in gear motor systems. The following approaches can help address this issue:
- Anti-Backlash Gears: Using anti-backlash gears, which are designed to minimize or eliminate backlash, can significantly reduce inaccuracies caused by gear play.
- Tight Manufacturing Tolerances: Ensuring precise manufacturing tolerances during gear production helps minimize backlash and improve overall accuracy.
- Backlash Compensation: Implementing control algorithms or mechanisms to compensate for backlash can help mitigate its effects and improve the accuracy of the gear motor.
3. Noise and Vibrations:
Gear motors can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which may be undesirable in certain applications. The following strategies can help mitigate this challenge:
- Noise Dampening: Incorporating noise-dampening features, such as vibration-absorbing materials or isolation mounts, can reduce noise and vibrations transmitted from the gear motor to the surrounding environment.
- Quality Gears and Bearings: Using high-quality gears and bearings can minimize vibrations and noise generation. Precision-machined gears and well-maintained bearings help ensure smooth operation and reduce unwanted noise.
- Proper Alignment: Ensuring accurate alignment of gears, shafts, and other components reduces the likelihood of noise and vibrations caused by misalignment. Regular inspections and adjustments can help maintain optimal alignment.
4. Overheating and Thermal Management:
Heat buildup can be a challenge in gear motors, especially during prolonged or heavy-duty operation. Effective thermal management techniques can address this issue:
- Adequate Ventilation: Providing proper ventilation and airflow around the gear motor helps dissipate heat. This can involve designing cooling fins, incorporating fans or blowers, or ensuring sufficient clearance for air circulation.
- Heat Dissipation Materials: Using heat-dissipating materials, such as aluminum or copper, in motor housings or heat sinks can improve heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Monitoring and Control: Implementing temperature sensors and thermal protection mechanisms allows for real-time monitoring of the gear motor’s temperature. If the temperature exceeds safe limits, the motor can be automatically shut down or adjusted to prevent damage.
5. Load Variations and Shock Loads:
Unexpected load variations or shock loads can impact the performance and durability of gear motors. The following measures can help address this challenge:
- Proper Sizing and Selection: Choosing gear motors with appropriate torque and load capacity ratings for the intended application helps ensure they can handle expected load variations and occasional shock loads without exceeding their limits.
- Shock Absorption: Incorporating shock-absorbing mechanisms, such as dampers or resilient couplings, can help mitigate the effects of sudden load changes or impacts on the gear motor.
- Load Monitoring: Implementing load monitoring systems or sensors allows for real-time monitoring of load variations. This information can be used to adjust operation or trigger protective measures when necessary.
By addressing these common challenges associated with gear motors through appropriate design considerations, regular maintenance, and operational practices, it is possible to enhance their performance, reliability, and longevity.

In which industries are gear motors commonly used, and what are their primary applications?
Gear motors find widespread use in various industries due to their versatility, reliability, and ability to provide controlled mechanical power. They are employed in a wide range of applications that require precise power transmission and speed control. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries where gear motors are commonly used and their primary applications:
1. Robotics and Automation:
Gear motors play a crucial role in robotics and automation industries. They are used in robotic arms, conveyor systems, automated assembly lines, and other robotic applications. Gear motors provide the required torque, speed control, and directional control necessary for the precise movements and operations of robots. They enable accurate positioning, gripping, and manipulation tasks in industrial and commercial automation settings.
2. Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry extensively utilizes gear motors in various applications. They are used in power windows, windshield wipers, HVAC systems, seat adjustment mechanisms, and many other automotive components. Gear motors provide the necessary torque and speed control for these systems, enabling smooth and efficient operation. Additionally, gear motors are also utilized in electric and hybrid vehicles for powertrain applications.
3. Manufacturing and Machinery:
Gear motors find wide application in the manufacturing and machinery sector. They are used in conveyor belts, packaging equipment, material handling systems, industrial mixers, and other machinery. Gear motors provide reliable power transmission, precise speed control, and torque amplification, ensuring efficient and synchronized operation of various manufacturing processes and machinery.
4. HVAC and Building Systems:
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, gear motors are commonly used in damper actuators, control valves, and fan systems. They enable precise control of airflow, temperature, and pressure, contributing to energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. Gear motors also find applications in automatic doors, blinds, and gate systems, providing reliable and controlled movement.
5. Marine and Offshore Industry:
Gear motors are extensively used in the marine and offshore industry, particularly in propulsion systems, winches, and cranes. They provide the required torque and speed control for various marine operations, including steering, anchor handling, cargo handling, and positioning equipment. Gear motors in marine applications are designed to withstand harsh environments and provide reliable performance under demanding conditions.
6. Renewable Energy Systems:
The renewable energy sector, including wind turbines and solar tracking systems, relies on gear motors for efficient power generation. Gear motors are used to adjust the rotor angle and position in wind turbines, optimizing their performance in different wind conditions. In solar tracking systems, gear motors enable the precise movement and alignment of solar panels to maximize sunlight capture and energy production.
7. Medical and Healthcare:
Gear motors have applications in the medical and healthcare industry, including in medical equipment, laboratory devices, and patient care systems. They are used in devices such as infusion pumps, ventilators, surgical robots, and diagnostic equipment. Gear motors provide precise control and smooth operation, ensuring accurate dosing, controlled movements, and reliable functionality in critical medical applications.
These are just a few examples of the industries where gear motors are commonly used. Their versatility and ability to provide controlled mechanical power make them indispensable in numerous applications requiring torque amplification, speed control, directional control, and load distribution. The reliable and efficient power transmission offered by gear motors contributes to the smooth and precise operation of machinery and systems in various industries.


editor by CX 2024-04-11
China factory DC 12V 24V with Gear Reduction 24byj48 Stepping Motor, DC Micro Worm Gear Motor, 24mm Diameter Stepper Motor for IP Camera vacuum pump oil near me
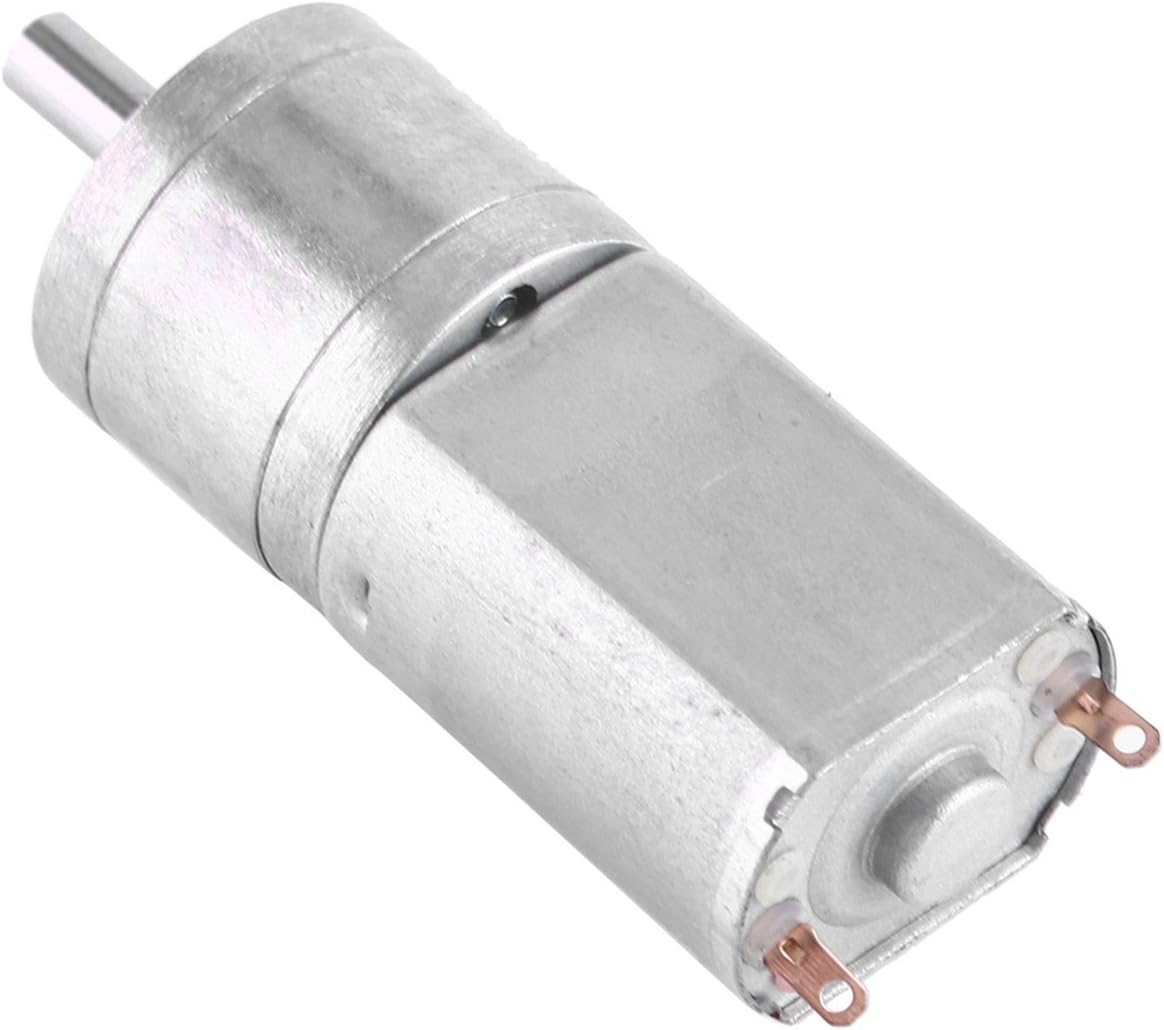
Product Description
Product Description
We are professional manufacturer for 20BYJ46 / 24BYJ / 28BYJ48 / 24BYJ48 / 30BYJ / 30BYJ46 / 35BYJ46 / 35BYJ412 series stepper motor
Motor voltage, speed, pull the torque, can be adjusted according to customer requirements.
Products are widely used in air conditioning, monitoring, smart toilet, electronic locks, valves, packaging machinery, food machinery, printing machinery, semiconductor processing, medical machinery, textile machinery, office automation equipment, fitness equipment,Engraved, lettering, and other areas of automation and control. We also serve the user at the same time, to provide the entire system control program, motor selection and technical support for the motor control, to undertake the motor control system hardware and software development.
Mainly used for: home air conditioning, surveillance cameras, high-speed dome, variable speed ball, medium speed ball, air conditioning, smart toilet, office equipment, mobile air conditioning, stage lighting, medical equipment, textile machinery, equipment, sanitary ware and other automation and control areas.
General models are as follows:
| V | Ω | HZ | ≥mN.m | ≥mN.m | pps | pps | step angle | |
| 24BYJ48 | 5 | 15 | 100 | 24.5 | 24.5 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 5 | 15 | 100 | 29.4 | 39.4 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 5 | 20 | 100 | 34.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 5 | 20 | 100 | 88.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 12 | 80 | 100 | 98 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 12 | 120 | 100 | 88.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 12 | 200 | 100 | 68.6 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 12 | 300 | 100 | 49 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 24 | 200 | 100 | 98 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 24 | 300 | 100 | 88.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 24BYJ48 | 36 | 380 | 100 | 98 | 49 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| Reduction ratio:1/12 1/16 1/25 1/32 1/36 1/64 1/90 1/96 | ||||||||
| 28BYJ48 | 5 | 15 | 100 | 24.5 | 24.5 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 5 | 15 | 100 | 29.4 | 39.4 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 5 | 20 | 100 | 34.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 5 | 20 | 100 | 88.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 12 | 80 | 100 | 98 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 12 | 130 | 100 | 88.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 12 | 200 | 100 | 68.6 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 12 | 300 | 100 | 49 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 24 | 200 | 100 | 98 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 24 | 300 | 100 | 88.2 | 39.2 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| 28BYJ48 | 36 | 380 | 100 | 98 | 49 | 800 | 1000 | 5.625 |
| Reduction ratio:1/12 1/16 1/25 1/32 1/36 1/64 1/90 1/96 | ||||||||
| 35BYJ46 | 5 | 10–20 | 100 | 127-196 | 58.8 | 800 | 500 | 7.5 |
| 35BYJ46 | 12 | 30-60 | 100 | 196 | 88.2 | 800 | 500 | 7.5 |
| 35BYJ46 | 12 | 70-100 | 100 | 147 | 68.8 | 800 | 500 | 7.5 |
| 35BYJ46 | 12 | 130 | 100 | 127.4 | 68.8 | 800 | 500 | 7.5 |
| 35BYJ46 | 12 | 200 | 100 | 147 | 68.8 | 800 | 500 | 7.5 |
| 35BYJ46 | 24 | 250 | 100 | 196 | 88.2 | 800 | 500 | 7.5 |
| Reduction ratio:1/15 1/30 1/85 | ||||||||
| 35BYJ412 | 5 | 15-20 | 100 | 300 | 120 | 500 | 350 | 3.75 |
| 35BYJ412 | 12 | 40-60 | 100 | 350 | 120 | 500 | 350 | 3.75 |
| 35BYJ412 | 12 | 70-90 | 100 | 350 | 150 | 500 | 350 | 3.75 |
| 35BYJ412 | 12 | 100-120 | 100 | 300 | 150 | 500 | 350 | 3.75 |
| 35BYJ412 | 12 | 130-150 | 100 | 300 | 180 | 500 | 350 | 3.75 |
| 35BYJ412 | 24 | 200-600 | 100 | 300 | 180 | 500 | 350 | 3.75 |
| Reduction ratio:1/17.7 1/22.3 1/42.5 | ||||||||
After-Sales Service
All of our motors have a Warranty and complete After-Sales Service:
1). If there are any quality problems in 1 month when customer received our motors, we will send you new motors to replace the defective ones, We pay for all of the cost; or we refund all of the payment to customer.
2). All of our motor’s information, such as specification data, and instructions of usage will be offered to customer.
1.Q: Can I get some samples first?
A: Sure, we are honored to offer you samples for your check.
2.Q: Do you have the products in stock?
A: Our products are manufactured according to your order except for the normal products.
3.Q: What’s the delivery time?
A: It usually takes about 7 working days,but the exact delivery time might be different for different orders or at different time.
4.Q: How does your factory do regarding quality control?
A: Quality is a priority. We always attach great importance to quality control from the beginning to the end of production. Every product will be fully assembled and carefully tested before being packed.
5.Q: What are your warranty terms?
A: We offer different warranty terms for different products. Please contact us for details. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Air Conditioner, Bidet, Fans, Purifier |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Number of Stator: | Four-Phase |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What are the maintenance requirements for gear motors, and how can longevity be maximized?
Gear motors, like any mechanical system, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance practices help prevent failures, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of gear motors. Here are some maintenance requirements for gear motors and ways to maximize their longevity:
1. Lubrication:
Regular lubrication is essential for gear motors to reduce friction, wear, and heat generation. The gears, bearings, and other moving parts should be properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Lubricants should be selected based on the motor’s specifications and operating conditions. Regular inspection and replenishment of lubricants, as well as periodic oil or grease changes, should be performed to maintain optimal lubrication levels and ensure long-lasting performance.
2. Inspection and Cleaning:
Regular inspection and cleaning of gear motors are crucial for identifying any signs of wear, damage, or contamination. Inspecting the gears, bearings, shafts, and connections can help detect any abnormalities or misalignments. Cleaning the motor’s exterior and ventilation channels to remove dust, debris, or moisture buildup is also important in preventing malfunctions and maintaining proper cooling. Any loose or damaged components should be repaired or replaced promptly.
3. Temperature and Environmental Considerations:
Monitoring and controlling the temperature and environmental conditions surrounding gear motors can significantly impact their longevity. Excessive heat can degrade lubricants, damage insulation, and lead to premature component failure. Ensuring proper ventilation, heat dissipation, and avoiding overloading the motor can help manage temperature effectively. Similarly, protecting gear motors from moisture, dust, chemicals, and other environmental contaminants is vital to prevent corrosion and damage.
4. Load Monitoring and Optimization:
Monitoring and optimizing the load placed on gear motors can contribute to their longevity. Operating gear motors within their specified load and speed ranges helps prevent excessive stress, overheating, and premature wear. Avoiding sudden and frequent acceleration or deceleration, as well as preventing overloading or continuous operation near the motor’s maximum capacity, can extend its lifespan.
5. Alignment and Vibration Analysis:
Proper alignment of gear motor components, such as gears, couplings, and shafts, is crucial for smooth and efficient operation. Misalignment can lead to increased friction, noise, and premature wear. Regularly checking and adjusting alignment, as well as performing vibration analysis, can help identify any misalignment or excessive vibration that may indicate underlying issues. Addressing alignment and vibration problems promptly can prevent further damage and maximize the motor’s longevity.
6. Preventive Maintenance and Regular Inspections:
Implementing a preventive maintenance program is essential for gear motors. This includes establishing a schedule for routine inspections, lubrication, and cleaning, as well as conducting periodic performance tests and measurements. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for maintenance tasks, such as belt tension checks, bearing replacements, or gear inspections, can help identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major failures.
By adhering to these maintenance requirements and best practices, the longevity of gear motors can be maximized. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, load optimization, temperature control, and timely repairs or replacements of worn components contribute to the reliable operation and extended lifespan of gear motors.

Can gear motors be used for precise positioning, and if so, what features enable this?
Yes, gear motors can be used for precise positioning in various applications. The combination of gear mechanisms and motor control features enables gear motors to achieve accurate and repeatable positioning. Here’s a detailed explanation of the features that enable gear motors to be used for precise positioning:
1. Gear Reduction:
One of the key features of gear motors is their ability to provide gear reduction. Gear reduction refers to the process of reducing the output speed of the motor while increasing the torque. By using the appropriate gear ratio, gear motors can achieve finer control over the rotational movement, allowing for more precise positioning. The gear reduction mechanism enables the motor to rotate at a slower speed while maintaining higher torque, resulting in improved accuracy and control.
2. High Resolution Encoders:
Many gear motors are equipped with high-resolution encoders. An encoder is a device that measures the position and speed of the motor shaft. High-resolution encoders provide precise feedback on the motor’s rotational position, allowing for accurate position control. The encoder signals are used in conjunction with motor control algorithms to ensure precise positioning by monitoring and adjusting the motor’s movement in real-time. The use of high-resolution encoders greatly enhances the gear motor’s ability to achieve precise and repeatable positioning.
3. Closed-Loop Control:
Gear motors with closed-loop control systems offer enhanced positioning capabilities. Closed-loop control involves continuously comparing the actual motor position (as measured by the encoder) with the desired position and making adjustments to minimize any position error. The closed-loop control system uses feedback from the encoder to adjust the motor’s speed, direction, and torque, ensuring accurate positioning even in the presence of external disturbances or variations in the load. Closed-loop control enables gear motors to actively correct for position errors and maintain precise positioning over time.
4. Stepper Motors:
Stepper motors are a type of gear motor that provides excellent precision and control for positioning applications. Stepper motors operate by converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement. Each step corresponds to a specific angular displacement, allowing precise positioning control. Stepper motors offer high step resolution, allowing for fine position adjustments. They are commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics, 3D printers, and CNC machines.
5. Servo Motors:
Servo motors are another type of gear motor that excels in precise positioning tasks. Servo motors combine a motor, a feedback device (such as an encoder), and a closed-loop control system. They offer high torque, high speed, and excellent positional accuracy. Servo motors are capable of dynamically adjusting their speed and torque to maintain the desired position accurately. They are widely used in applications that require precise and responsive positioning, such as industrial automation, robotics, and camera pan-tilt systems.
6. Motion Control Algorithms:
Advanced motion control algorithms play a crucial role in enabling gear motors to achieve precise positioning. These algorithms, implemented in motor control systems or dedicated motion controllers, optimize the motor’s behavior to ensure accurate positioning. They take into account factors such as acceleration, deceleration, velocity profiling, and jerk control to achieve smooth and precise movements. Motion control algorithms enhance the gear motor’s ability to start, stop, and position accurately, reducing position errors and overshoot.
By leveraging gear reduction, high-resolution encoders, closed-loop control, stepper motors, servo motors, and motion control algorithms, gear motors can be effectively used for precise positioning in various applications. These features enable gear motors to achieve accurate and repeatable positioning, making them suitable for tasks that require precise control and reliable positioning performance.

In which industries are gear motors commonly used, and what are their primary applications?
Gear motors find widespread use in various industries due to their versatility, reliability, and ability to provide controlled mechanical power. They are employed in a wide range of applications that require precise power transmission and speed control. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries where gear motors are commonly used and their primary applications:
1. Robotics and Automation:
Gear motors play a crucial role in robotics and automation industries. They are used in robotic arms, conveyor systems, automated assembly lines, and other robotic applications. Gear motors provide the required torque, speed control, and directional control necessary for the precise movements and operations of robots. They enable accurate positioning, gripping, and manipulation tasks in industrial and commercial automation settings.
2. Automotive Industry:
The automotive industry extensively utilizes gear motors in various applications. They are used in power windows, windshield wipers, HVAC systems, seat adjustment mechanisms, and many other automotive components. Gear motors provide the necessary torque and speed control for these systems, enabling smooth and efficient operation. Additionally, gear motors are also utilized in electric and hybrid vehicles for powertrain applications.
3. Manufacturing and Machinery:
Gear motors find wide application in the manufacturing and machinery sector. They are used in conveyor belts, packaging equipment, material handling systems, industrial mixers, and other machinery. Gear motors provide reliable power transmission, precise speed control, and torque amplification, ensuring efficient and synchronized operation of various manufacturing processes and machinery.
4. HVAC and Building Systems:
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, gear motors are commonly used in damper actuators, control valves, and fan systems. They enable precise control of airflow, temperature, and pressure, contributing to energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. Gear motors also find applications in automatic doors, blinds, and gate systems, providing reliable and controlled movement.
5. Marine and Offshore Industry:
Gear motors are extensively used in the marine and offshore industry, particularly in propulsion systems, winches, and cranes. They provide the required torque and speed control for various marine operations, including steering, anchor handling, cargo handling, and positioning equipment. Gear motors in marine applications are designed to withstand harsh environments and provide reliable performance under demanding conditions.
6. Renewable Energy Systems:
The renewable energy sector, including wind turbines and solar tracking systems, relies on gear motors for efficient power generation. Gear motors are used to adjust the rotor angle and position in wind turbines, optimizing their performance in different wind conditions. In solar tracking systems, gear motors enable the precise movement and alignment of solar panels to maximize sunlight capture and energy production.
7. Medical and Healthcare:
Gear motors have applications in the medical and healthcare industry, including in medical equipment, laboratory devices, and patient care systems. They are used in devices such as infusion pumps, ventilators, surgical robots, and diagnostic equipment. Gear motors provide precise control and smooth operation, ensuring accurate dosing, controlled movements, and reliable functionality in critical medical applications.
These are just a few examples of the industries where gear motors are commonly used. Their versatility and ability to provide controlled mechanical power make them indispensable in numerous applications requiring torque amplification, speed control, directional control, and load distribution. The reliable and efficient power transmission offered by gear motors contributes to the smooth and precise operation of machinery and systems in various industries.


editor by CX 2024-03-27
China Custom 42 mm (NEMA 17) Electrical Hybrid Stepper Stepping Motor for 3D Printer manufacturer
Product Description
Note:
The specifications can be designed according to the customer’s requirements!
Option:
Customized shaft, performance, voltage, lead wires…
Application:
Robots, Electric Automatic Equipment, Medical Instrument, Advertisement Instrument, Lighting& audio Equipment, Printer, Textile Machinery, CNC Router, 3D Printer.
Parameter:
Electrical Specification:
| Series Model | Step Angle ( o ) | L (mm) |
Rated Current (A) | Phase Resistance ( Ω ) |
Phase Inductance (mH) |
Holding Torque (N.cm) |
Detent Torque (N.cm) | Lead Wire (NO.) |
Motor Weight ( g) |
| H421-01206 | 1.8 | 28 | 0.6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 1.6 | 4 | 150 |
| H421-57113 | 1.8 | 34 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 28 | 1.6 | 4 | 220 |
| H421-57117 | 1.8 | 34 | 1.7 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 28 | 1.6 | 4 | 220 |
| H421-57104 | 1.8 | 34 | 0.4 | 30 | 35 | 28 | 1.6 | 4 | 220 |
| H421-57104 | 1.8 | 34 | 0.4 | 30 | 18 | 21 | 1.6 | 6 | 220 |
| H421-01402 | 1.8 | 34 | 0.16 | 75 | 40 | 14 | 1.6 | 6 | 220 |
| H421-04017 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 2.8 | 40 | 2.2 | 4 | 280 |
| H421-04013 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.3 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 40 | 2.2 | 4 | 280 |
| H421-57112 | 1.8 | 40 | 1.2 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 28 | 2.2 | 6 | 280 |
| H421-57104 | 1.8 | 40 | 0.4 | 30 | 28 | 28 | 2.2 | 6 | 280 |
| H421-571 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 52 | 2.6 | 4 | 350 |
| H421-05213 | 1.8 | 48 | 1.3 | 3.2 | 5.5 | 52 | 2.6 | 4 | 350 |
| H421-05223 | 1.8 | 48 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 52 | 2.6 | 4 | 350 |
| H421-03404 | 1.8 | 48 | 0.4 | 30 | 38 | 34 | 2.6 | 6 | 350 |
| H | 1.8 | 58 | 1.2 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 54 | 3.2 | 6 | 450 |
About Us:
I.CH motion co., LTD, headquartered in HangZhou, is a professional manufacturer and supplier of the motor. We have provided Hybrid stepper motor, stepper gear motor, BLDC motor, BLDC Gear motor, BLDC Servo motor since 2006, which are widely used in medical equipment, automation equipment, automobile industry, and 3D printer.
As a professional manufacturer who has professional teams, we can custom according to your needs.
Work-flow:
Certificate:
IOS9001, CE…
Service:
1, OEM & ODM service.
2, One-year guarantee.
Shipping:
1, Inside: High-density foam box
outside: hardboard carton box.
2, The Delivery time is about 30-45 days.
Customer’s Visiting:
FAQ:
1, Are you a factory?
Yes, we have been in designing and providing excellent motors for customers.
2, Can you provide a sample?
Yes.
3, How long you could prepare samples?
If customized one, about a week around.
4, If My package has missing products. What can I do?
Please contact our support team and we will confirm your order with the package contents. We apologize for any inconvenience.
| Application: | Printing Equipment |
|---|---|
| Speed: | Low Speed |
| Function: | Control, Driving |
| Certification: | ISO9001, CCC |
| Brand: | I.CH |
| Lead Time: | 30-45 Days |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

Can gear motors be used in robotics, and if so, what are some notable applications?
Yes, gear motors are widely used in robotics due to their ability to provide torque, precise control, and compact size. They play a crucial role in various robotic applications, enabling the movement, manipulation, and control of robotic systems. Here are some notable applications of gear motors in robotics:
1. Robotic Arm Manipulation:
Gear motors are commonly used in robotic arms to provide precise and controlled movement. They enable the articulation of the arm’s joints, allowing the robot to reach different positions and orientations. Gear motors with high torque capabilities are essential for lifting, rotating, and manipulating objects with varying weights and sizes.
2. Mobile Robots:
Gear motors are employed in mobile robots, including wheeled robots and legged robots, to drive their locomotion. They provide the necessary torque and control for the robot to move, turn, and navigate in different environments. Gear motors with appropriate gear ratios ensure the robot’s mobility, stability, and maneuverability.
3. Robotic Grippers and End Effectors:
Gear motors are used in robotic grippers and end effectors to control the opening, closing, and gripping force. By integrating gear motors into the gripper mechanism, robots can grasp and manipulate objects of various shapes, sizes, and weights. The gear motors enable precise control over the gripping action, allowing the robot to handle delicate or fragile objects with care.
4. Autonomous Drones and UAVs:
Gear motors are utilized in the propulsion systems of autonomous drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They drive the propellers or rotors, providing the necessary thrust and control for the drone’s flight. Gear motors with high power-to-weight ratios, efficient energy conversion, and precise speed control are crucial for achieving stable and maneuverable flight in drones.
5. Humanoid Robots:
Gear motors are integral to the movement and functionality of humanoid robots. They are used in robotic joints, such as hips, knees, and shoulders, to enable human-like movements. Gear motors with appropriate torque and speed capabilities allow humanoid robots to walk, run, climb stairs, and perform complex motions resembling human actions.
6. Robotic Exoskeletons:
Gear motors play a vital role in robotic exoskeletons, which are wearable robotic devices designed to augment human strength and assist in physical tasks. Gear motors are used in the exoskeleton’s joints and actuators, providing the necessary torque and control to enhance human abilities. They enable users to perform tasks with reduced effort, assist in rehabilitation, or provide support in physically demanding environments.
These are just a few notable applications of gear motors in robotics. Their versatility, torque capabilities, precise control, and compact size make them indispensable components in various robotic systems. Gear motors enable robots to perform complex tasks, move with agility, interact with the environment, and assist humans in a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to healthcare and exploration.

How does the voltage and power rating of a gear motor impact its suitability for different tasks?
The voltage and power rating of a gear motor are important factors that influence its suitability for different tasks. These specifications determine the motor’s electrical characteristics and its ability to perform specific tasks effectively. Here’s a detailed explanation of how voltage and power rating impact the suitability of a gear motor for different tasks:
1. Voltage Rating:
The voltage rating of a gear motor refers to the electrical voltage it requires to operate optimally. Here’s how the voltage rating affects suitability:
- Compatibility with Power Supply: The gear motor’s voltage rating must match the available power supply. Using a motor with a voltage rating that is too high or too low for the power supply can lead to improper operation or damage to the motor.
- Electrical Safety: Adhering to the specified voltage rating ensures electrical safety. Using a motor with a higher voltage rating than recommended can pose safety hazards, while using a motor with a lower voltage rating may result in inadequate performance.
- Application Flexibility: Different tasks or applications may have specific voltage requirements. For example, low-voltage gear motors are commonly used in battery-powered devices or applications with low-power requirements, while high-voltage gear motors are suitable for industrial applications or tasks that require higher power output.
2. Power Rating:
The power rating of a gear motor indicates its ability to deliver mechanical power. It is typically specified in units of watts (W) or horsepower (HP). The power rating impacts the suitability of a gear motor in the following ways:
- Load Capacity: The power rating determines the maximum load that a gear motor can handle. Motors with higher power ratings are capable of driving heavier loads or handling tasks that require more torque.
- Speed and Torque: The power rating affects the motor’s speed and torque characteristics. Motors with higher power ratings generally offer higher speeds and greater torque output, making them suitable for applications that require faster operation or the ability to overcome higher resistance or loads.
- Efficiency and Energy Consumption: The power rating is related to the motor’s efficiency and energy consumption. Higher power-rated motors may be more efficient, resulting in lower energy losses and reduced operating costs over time.
- Thermal Considerations: Motors with higher power ratings may generate more heat during operation. It is crucial to consider the motor’s power rating in relation to its thermal management capabilities to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability.
Considerations for Task Suitability:
When selecting a gear motor for a specific task, it is important to consider the following factors in relation to the voltage and power rating:
- Required Torque and Load: Assess the torque and load requirements of the task to ensure that the gear motor’s power rating is sufficient to handle the expected load without being overloaded.
- Speed and Precision: Consider the desired speed and precision of the task. Motors with higher power ratings generally offer better speed control and accuracy.
- Power Supply Availability: Evaluate the availability and compatibility of the power supply with the gear motor’s voltage rating. Ensure that the power supply can provide the required voltage for the motor’s optimal operation.
- Environmental Factors: Consider any specific environmental factors, such as temperature or humidity, that may impact the gear motor’s performance. Ensure that the motor’s voltage and power ratings are suitable for the intended operating conditions.
In summary, the voltage and power rating of a gear motor have significant implications for its suitability in different tasks. The voltage rating determines compatibility with the power supply and ensures electrical safety, while the power rating influences load capacity, speed, torque, efficiency, and thermal considerations. When choosing a gear motor, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the task requirements and consider the voltage and power rating in relation to factors such as torque, speed, power supply availability, and environmental conditions.

Are there specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application?
When selecting a gear motor for a specific application, several considerations need to be taken into account. The choice of the right gear motor is crucial to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the specific considerations for selecting the right gear motor for a particular application:
1. Torque Requirement:
The torque requirement of the application is a critical factor in gear motor selection. Determine the maximum torque that the gear motor needs to deliver to perform the required tasks. Consider both the starting torque (the torque required to initiate motion) and the operating torque (the torque required to sustain motion). Select a gear motor that can provide adequate torque to handle the load requirements of the application. It’s important to account for any potential torque spikes or variations during operation.
2. Speed Requirement:
Consider the desired speed range or specific speed requirements of the application. Determine the rotational speed (in RPM) that the gear motor needs to achieve to meet the application’s performance criteria. Select a gear motor with a suitable gear ratio that can achieve the desired speed at the output shaft. Ensure that the gear motor can maintain the required speed consistently and accurately throughout the operation.
3. Duty Cycle:
Evaluate the duty cycle of the application, which refers to the ratio of operating time to rest or idle time. Consider whether the application requires continuous operation or intermittent operation. Determine the duty cycle’s impact on the gear motor, including factors such as heat generation, cooling requirements, and potential wear and tear. Select a gear motor that is designed to handle the expected duty cycle and ensure long-term reliability and durability.
4. Environmental Factors:
Take into account the environmental conditions in which the gear motor will operate. Consider factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, dust, vibrations, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances. Choose a gear motor that is specifically designed to withstand and perform optimally under the anticipated environmental conditions. This may involve selecting gear motors with appropriate sealing, protective coatings, or materials that can resist corrosion and withstand harsh environments.
5. Efficiency and Power Requirements:
Consider the desired efficiency and power consumption of the gear motor. Evaluate the power supply available for the application and select a gear motor that operates within the specified voltage and current ranges. Assess the gear motor’s efficiency to ensure that it maximizes power transmission and minimizes wasted energy. Choosing an efficient gear motor can contribute to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
6. Physical Constraints:
Assess the physical constraints of the application, including space limitations, mounting options, and integration requirements. Consider the size, dimensions, and weight of the gear motor to ensure it can be accommodated within the available space. Evaluate the mounting options and compatibility with the application’s mechanical structure. Additionally, consider any specific integration requirements, such as shaft dimensions, connectors, or interfaces that need to align with the application’s design.
7. Noise and Vibration:
Depending on the application, noise and vibration levels may be critical factors. Evaluate the acceptable noise and vibration levels for the application’s environment and operation. Choose a gear motor that is designed to minimize noise and vibration, such as those with helical gears or precision engineering. This is particularly important in applications that require quiet operation or where excessive noise and vibration may cause issues or discomfort.
By considering these specific factors when selecting a gear motor for a particular application, you can ensure that the chosen gear motor meets the performance requirements, operates efficiently, and provides reliable and consistent power transmission. It’s important to consult with gear motor manufacturers or experts to determine the most suitable gear motor based on the specific application’s needs.


editor by CX 2023-12-12
China Transmission Motor Gearbox Unit Wp Nmrv Swl Screw Drive Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Planetary Bevel Worm Speed Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox with Hot selling
Item Description
Transmission Motor Gearbox Device Wp Nmrv Swl Screw Travel Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Planetary Bevel Worm Pace Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox
Attributes
1. Compact framework and straightforward assembly
two. Vast velocity ranges and high torque
three. Lower sounds, good sealing efficiency, substantial performance
4. Steady and safe, lengthy lifetime, common
five. Multi-construction, a variety of assembling methods
Product Photos
Product Description
| ANG Helical Equipment Reducer | |
| Product | R17 ~ 187, F37-177, K37-187, S37-ninety seven, HB01-26 |
| Input energy | .06kw ~ 5000kw |
| Enter speed | 750rpm ~ 3000rpm |
| Reduction ratio | one/1.3 ~ 1/27000 |
| Enter motor | AC (1 period or 3 period) / DC / BLDC motor |
| Put in sort | Foot / Sound shaft / Hollow shaft / Output flange… |
| Efficiency | 94% ~ ninety eight % for R F K series |
| Content of housing | die-solid aluminum / Cast iron / Stainless steel |
| Precision of equipment | Correct grinding, class six |
| Warmth treatment | Carburizing and quenching |
| Add-ons | Brake / Flange / Motor adapter / Torque arm … |
Benefits
FAQ
Q: Can you make the gearbox with customization?
A: Sure, we can customize for each your ask for, like electricity, voltage, speed, shaft measurement, flange, terminal box, IP quality, and many others.
Q: Do you offer samples?
A: Yes. The sample is offered for screening.
Q: What is your MOQ?
A: It is 1pcs for the starting of our enterprise.
Q: What’s your guide time?
A: Normal product need to have 5-30days, a little bit more time for personalized items.
Q: Do you offer complex assist?
A: Yes. Our organization have style and growth group, we can give technological assistance if you
need to have.
Q: How to ship to us?
A: It is offered by air, or by sea, or by practice.
Q: How to spend the cash?
A: T/T and L/C are favored, with a various forex, such as USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know the solution is appropriate for me?
A: >1ST validate drawing and specification >2nd take a look at sample >3rd commence mass creation.
Q: Can I arrive to your company to check out?
A: Indeed, you are welcome to go to us at any time.
Q: How shall we speak to you?
A: You can send inquiry directly, and we will reply within 24 several hours.
|
US $100-300 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Change Drive Torque |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| ANG Helical Gear Reducer | |
| Model | R17 ~ 187, F37-177, K37-187, S37-97, HB01-26 |
| Input power | 0.06kw ~ 5000kw |
| Input speed | 750rpm ~ 3000rpm |
| Reduction ratio | 1/1.3 ~ 1/27000 |
| Input motor | AC (1 phase or 3 phase) / DC / BLDC motor |
| Install type | Foot / Solid shaft / Hollow shaft / Output flange… |
| Efficiency | 94% ~ 98 % for R F K series |
| Material of housing | die-cast aluminum / Cast iron / Stainless steel |
| Precision of gear | Accurate grinding, class 6 |
| Heat treatment | Carburizing and quenching |
| Accessories | Brake / Flange / Motor adapter / Torque arm … |
|
US $100-300 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Change Drive Torque |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Horizontal Type |
| Step: | Three-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 300/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| ANG Helical Gear Reducer | |
| Model | R17 ~ 187, F37-177, K37-187, S37-97, HB01-26 |
| Input power | 0.06kw ~ 5000kw |
| Input speed | 750rpm ~ 3000rpm |
| Reduction ratio | 1/1.3 ~ 1/27000 |
| Input motor | AC (1 phase or 3 phase) / DC / BLDC motor |
| Install type | Foot / Solid shaft / Hollow shaft / Output flange… |
| Efficiency | 94% ~ 98 % for R F K series |
| Material of housing | die-cast aluminum / Cast iron / Stainless steel |
| Precision of gear | Accurate grinding, class 6 |
| Heat treatment | Carburizing and quenching |
| Accessories | Brake / Flange / Motor adapter / Torque arm … |
Developing a Mathematical Model of a Cyclone Gearbox
Compared to planetary gearboxes, cycloidal gearboxes are often seen as the ideal choice for a wide range of applications. They feature compact designs that are often low friction and high reduction ratios.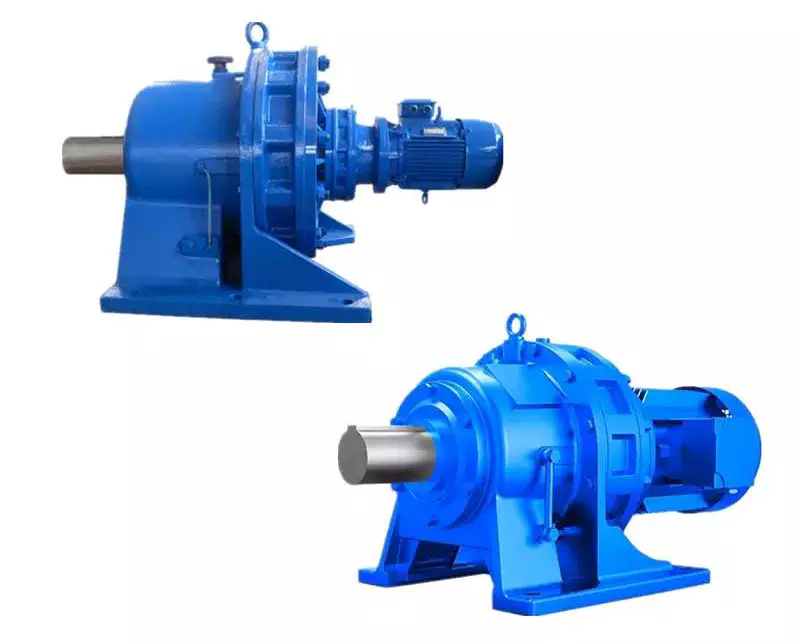
Low friction
Developing a mathematical model of a cycloidal gearbox was a challenge. The model was able to show the effects of a variety of geometric parameters on contact stresses. It was able to model stiction in all quadrants. It was able to show a clear correlation between the results from simulation and real-world measurements.
The model is based on a new approach that enables modeling stiction in all quadrants of a gearbox. It is also able to display non-zero current at standstill. Combined with a good simulation algorithm, the model can be used to improve the dynamic behaviour of a controlled system.
A cycloidal gearbox is a compact actuator used for industrial automation. This type of gearbox provides high gear ratios, low wear, and good torsional stiffness. In addition, it has good shock load capacity.
The model is based on cycloidal discs that engage with pins on a stationary ring gear. The resulting friction function occurs when the rotor begins to rotate. It also occurs when the rotor reverses its rotation. The model has two curves, one for motor and one for generator mode.
The trochoidal profile on the cycloidal disc’s periphery is required for proper mating of the rotating parts. In addition, the profile should be defined accurately. This will allow an even distribution of contact forces.
The model was used to compare the relative performance of a cycloidal gearbox with that of an involute gearbox. This comparison indicates that the cycloidal gearbox can withstand more load than an involute gearbox. It is also able to last longer. It is also able to produce high gear ratios in a small space.
The model used is able to capture the exact geometry of the parts. It can also allow a better analysis of stresses.
Compact
Unlike helical gearing, compact cycloidal gearboxes can provide higher reduction ratios. They are more compact and less weighty. In addition, they provide better positioning accuracy.
Cycloid drives provide high torque and load capacity. They are also very efficient and robust. They are ideal for applications with heavy loads or shock loads. They also feature low backlash and high torsional stiffness. Cycloid gearboxes are available in a variety of designs.
Cycloid discs are mounted on an eccentric input shaft, which drives them around a stationary ring gear. The ring gear consists of many pins, and the cycloidal disc moves one lobe for every rotation of the input shaft. The output shaft contains roller pins, which rotate around holes in the cycloidal disc.
Cycloid drives are ideally suited to heavy loads and shock loads. They have high torsional stiffness and high reduction ratios, making them very efficient. Cycloid gearboxes have low backlash and high torque and are very compact.
Cycloid gearboxes are used for a wide variety of applications, including marine propulsion systems, CNC machining centers, medical technology, and manipulation robots. They are especially useful in applications with critical positioning accuracy, such as surgical positioning systems. Cycloid gearboxes feature extremely low hysteresis loss and low backlash over extended periods of use.
Cycloid discs are usually designed with a reduced cycloid diameter to minimize unbalance forces at high speeds. Cycloid drives also feature minimal backlash, a high reduction ratio, and excellent positioning accuracy. Cycloid gearboxes also have a long service life, compared to other gear drives. Cycloid drives are highly robust, and offer higher reduction ratios than helical gear drives.
Cycloid gearboxes have a low cost and are easy to print. CZPT gearboxes are available in a wide range of sizes and can produce high torque on the output axis.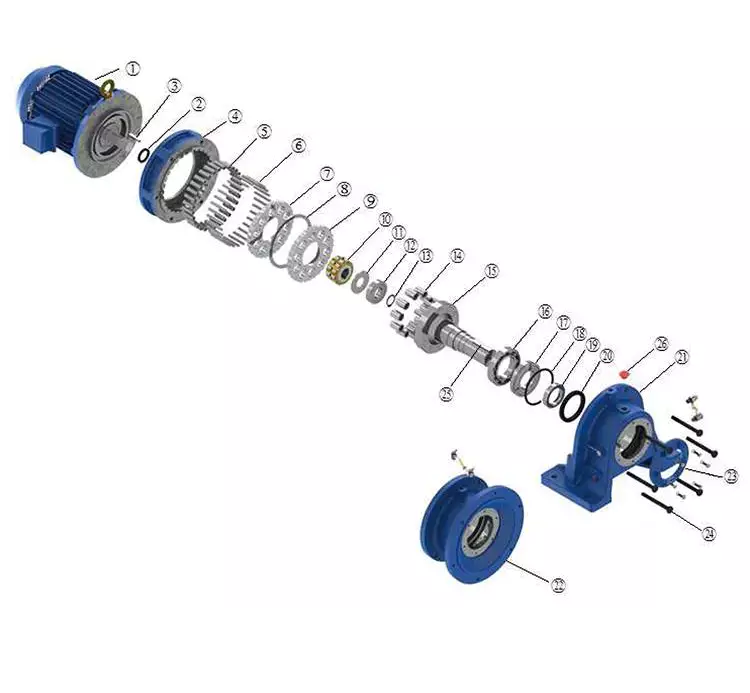
High reduction ratio
Among the types of gearboxes available, a high reduction ratio cycloidal gearbox is a popular choice in the automation field. This gearbox is used in applications requiring precise output and high efficiency.
Cycloid gears can provide high torque and transmit it well. They have low friction and a small backlash. They are widely used in robotic joints. However, they require special tools to manufacture. Some have even been 3D printed.
A cycloidal gearbox is typically a three-stage structure that includes an input hub, an output hub, and two cycloidal gears that rotate around each other. The input hub mounts movable pins and rollers, while the output hub mounts a stationary ring gear.
The input shaft is driven by an eccentric bearing. The disc is then pushed against the ring gear, which causes it to rotate around the bearing. As the disc rotates, the pins on the ring gear drive the pins on the output shaft.
The input shaft rotates a maximum of nine revolutions, while the output shaft rotates three revolutions. This means that the input shaft has to rotate over eleven million times before the output shaft is able to rotate. The output shaft also rotates in the opposite direction of the input shaft.
In a two-stage differential cycloidal speed reducer, the input shaft uses a crank shaft design. The crank shaft connects the first and second cycloidal gears and actuates them simultaneously.
The first stage is a cycloidal disc, which is a gear tooth profile. It has n=7 lobes on its circumference. Each lobe moves around a reference pitch circle of pins. The disc then advances in 360deg steps.
The second stage is a cycloidal disc, also known as a “grinder gear”. The teeth on the outer gear are fewer than the teeth on the inner gear. This allows the gear to be geardown based on the number of teeth.
Kinematics
Various scholars have studied the kinematics of cycloidal gearbox. They have developed various approaches to modify the tooth profile of cycloidal gears. Some of these approaches involve changing the shape of the cycloidal disc, and changing the grinding wheel center position.
This paper describes a new approach to cycloid gear profile modification. It is based on a mathematical model and incorporates several important parameters such as pressure angle, backlash, and root clearance. The study offers a new way for modification design of cycloid gears in precision reducers for robots.
The pressure angle of a tooth profile is an intersegment angle between the normal direction and the velocity direction at a meshing point. The pressure angle distribution is important for determining force transmission performance of gear teeth in meshing. The distribution trend can be obtained by calculating the equation (5).
The mathematical model for modification of the tooth profile can be obtained by establishing the relationship between the pressure angle distribution and the modification function. The dependent variable is the modification DL and the independent variable is the pressure angle a.
The position of the reference point A is a major consideration in the modification design. It ensures the force transmission performance of the meshing segment is optimal. It is determined by the smallest profile pressure angle. The position is also dependent on the type of gear that is being modified. It is also influenced by the tooth backlash.
The mathematical model governing the pressure angle distribution is developed with DL=f(a). It is a piecewise function that determines the pressure angle distribution of a tooth profile. It can also be expressed as DL=ph.
The pressure angle of a tooth is also an angle between the common normal direction at the meshing point and the rotation velocity direction of the cycloid gear.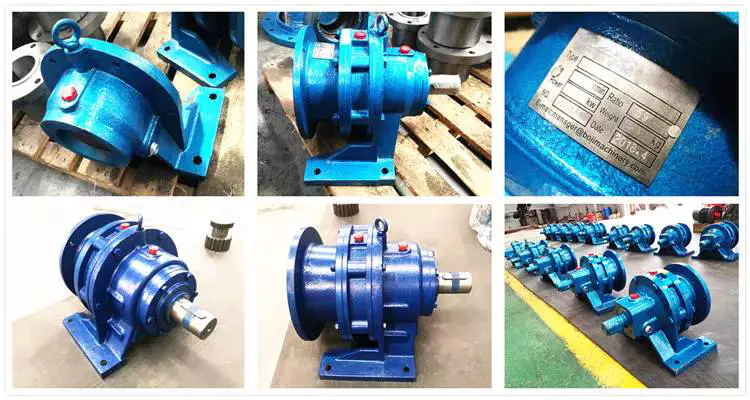
Planetary gearboxes vs cycloidal gearboxes
Generally, there are two types of gearboxes that are used for motion control applications: cycloidal gearbox and planetary gearbox. Cycloid gearboxes are used for high-frequency motions, while planetary gearboxes are suitable for low-speed applications. Both are highly accurate and precise gearboxes that are capable of handling heavy loads at high cycle rates. But they have different advantages and disadvantages. So, engineers need to determine which type of gearbox is best suited for their application.
Cycloid gearboxes are commonly used in industrial automation. They provide excellent performance with ratios as low as 10:1. They offer a more compact design, higher torque density and greater overload protection. They also require less space and are less expensive than planetary gearboxes.
On the other hand, planetary gearboxes are lightweight and offer a higher torque density. They are also capable of handling higher ratios. They have a longer life span and are more precise and durable. They can be found in a variety of styles, including square-framed, round-framed and double-frame designs. They offer a wide range of torque and speed capabilities and are used for numerous applications.
Cycloid gearboxes can be manufactured with different types of cycloidal cams, including single or compound cycloidal cams. Cycloid cams are cylindrical elements that have cam followers that rotate in an eccentric fashion. The cam followers act like teeth on the internal gear. Cycloid cams are a simple concept, but they have numerous advantages. They have a low backlash over extended periods of time, allowing for more accurate positioning. They also have internal compressive stresses and an overlap factor between the rolling elements.
Planetary gearboxes are characterized by three basic force-transmitting elements: ring gear, sun gear, and planet gear. They are generally two-stage gearboxes. The sun gear is attached to the input shaft, which in turn is attached to the servomotor. The ring gear turns the sun gear and the planet gear turns the output shaft.

editor by czh 2023-01-14
China Gpg Helical Precision Speed Reducer Planetary Gearbox for Servo Stepper Motor Tool Industrial Automation Robotics Laser Cutting Machine GB090-10-P2 Gvb78 gearbox definition
Product Description
TaiBang Motor Industry Group Co., Ltd.
The main products is induction motor, reversible motor, DC brush gear motor, DC brushless gear motor, CH/CV big gear motors, Planetary gear motor ,Worm gear motor etc, which used widely in various fields of manufacturing pipelining, transportation, food, medicine, printing, fabric, packing, office, apparatus, entertainment etc, and is the preferred and matched product for automatic machine.
Model Instruction
GB090-10-P2
| GB | 090 | 571 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
571 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precision Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
Main Technical Performance
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
Noise test standard:Distance 1m,no load.Measured with an input speed 3000rpm
|
US $50 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| GB | 090 | 010 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
010 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precision Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
###
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
###
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
|
US $50 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| GB | 090 | 010 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
010 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precision Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
###
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
###
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
Types of Gearboxes Used in Wind Turbines
Many manufacturers of wind turbines have chosen different solutions for the drive train of the turbines. Most prefer gearboxes because of their durability. These have several design features that make them well suited to shocks, stresses and wear. Regardless of the type of gearbox used, continuous maintenance and monitoring can extend the lifespan of these machines. Performing these tasks regularly can help detect and resolve any problems before they become serious. Here are some of the problems associated with gearboxes.
Coaxial helical gearbox
The R series helical inline gearbox is a high-quality speed reducer for heavy-duty industrial applications. These units are designed with increased power density in mind and are equipped with various cooling options. High-grade seals and lubricants help to increase efficiency and minimize thermal loading. They are ATEX-compliant. Their reversible modules are an excellent choice for high-speed applications, such as compressors, compressor blowers, and pumps.
The normal module set of helical gearbox is manufactured using the same tooth-cutting techniques as spur gears. This allows the production of higher-quality, more economical, and more compact helical gears. Although the performance of helical gears is lower than spur gears, they are durable and capable of transferring motion and power between two shafts. And because they are able to handle a much greater load, they are preferred for heavy-duty applications.
The main tooth form of a helical gearbox presents fixed velocity ratios, even if the center gap is not completely set. This requirement is sometimes referred to as the fundamental rule of gearing. A helical gearbox is similar to a set of paper spur gears, with the exception that the sections must stagger in opposite directions. There are two kinds of helical gears for parallel shafts: left-handed and right-handed.
The Industrial Gearbox market is segmented based on product type, application, and geography. The report analyzes the competitive scenario by segmenting the market by region, company, and type. Using this information, it estimates market size, revenue, and consumption. The report also features key information about COVID-19 and its impact on the overall industry. And it also provides a competitive landscape with industry-leading players.
Industrial gearboxes are integrated with devices and make automation processes more efficient and reliable. Increasing labor costs, shortage of skilled labor, and the ageing workforce are driving the demand for automation technologies. The industry requires newer and more advanced models and technologies to compete in the global market. You can use Coaxial helical gearbox in a variety of applications. Its benefits are endless. If you are looking for a reliable, high-performance industrial gearbox, CZPT can help you find it.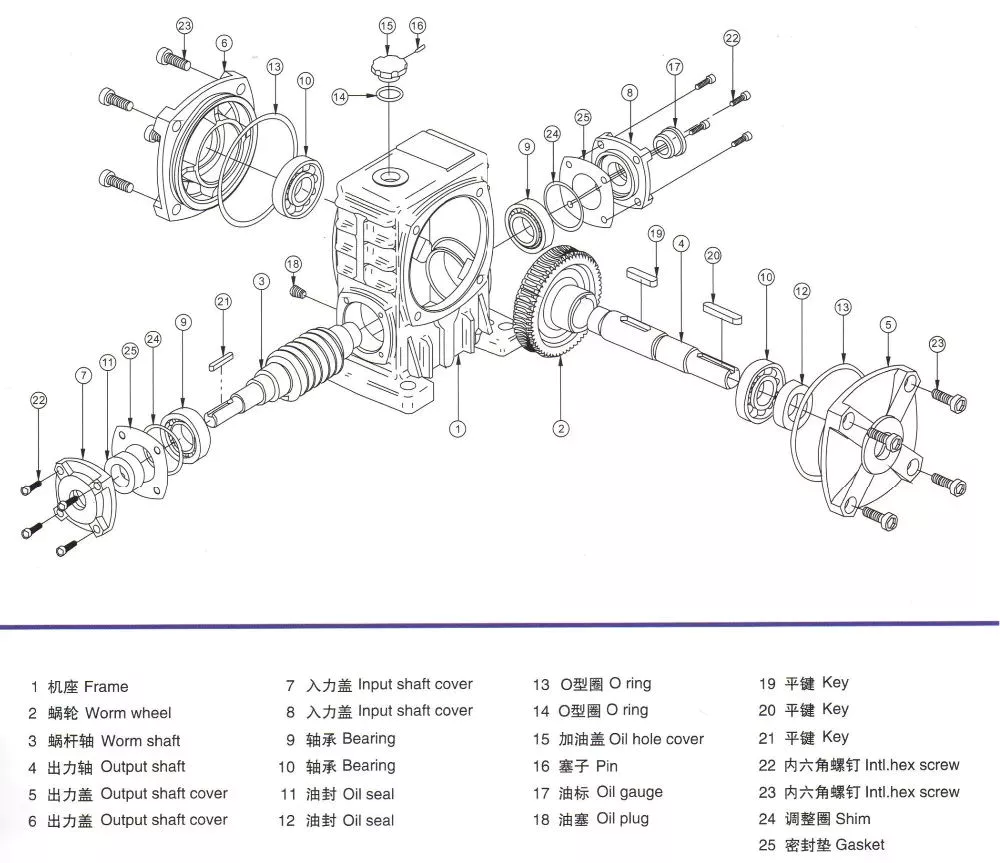
Worm reduction gearbox
As a general rule, larger center distance worm reduction gearboxes are more efficient than smaller ones. Worm gearboxes with 2.6-in. center distances start to lose efficiency as their ratios increase. Larger center distances tend to have higher efficiency than smaller ones. However, this difference may not always be enough to justify the higher investment. Worm gear reducers typically cost less than equivalent helical units.
The use of aluminum for worm reduction gearboxes is a popular choice for those involved in the manufacturing of Packaging Equipment. In addition to being lightweight, aluminum worm reduction gearboxes have high strength and rigidity. Manufacturers recommend this choice because of its high rigidity and durability. While purchasing aluminum worm reduction gearboxes, keep in mind that they are more expensive than steel versions. However, they have a longer lifespan and are highly resistant to wear.
The worm’s helix angle is larger than a helical gear, which allows a much higher gear ratio. In addition, the worm’s body is usually longer in the axial direction than helical gears. Worm reduction gears are often left-handed, and British or Indian standards are usually followed. The worm wheel is made of hardened alloy steel PB2-C, while the gearbox case is made of hardened alloy steel FG 220 or FG 250res.
The worms in a sacrificial system are relatively safe from wear. Instead, the softer wheel is the cause of most wear and tear. The oil analysis report for a sacrificial system shows low iron levels and high copper concentrations. However, if a worm reduction gearbox has a bad reputation, you should consider purchasing a new one. If the worm gears are in good condition, the gearbox is still a viable option for a new or replacement vehicle.
The advantages of a worm reduction gearbox are numerous. The worm gearbox is widely used in industrial settings, where it provides torque and speed reduction to move products. Worm gearboxes are also commonly used in automatic security gates, which will not run in reverse. Most security gates use two separate worm drives to keep the gate in the closed position. There are also many other uses for worm reducers. You can learn more about the benefits of worm gearboxes by reading below.
Stainless steel gearbox
Stainless steel gearboxes offer a number of advantages over standard gearboxes. They match the existing stainless motor design and cost 50 percent more on average. They have stainless output shafts and housings as well as corrosion resistant hardware and a food grade lubricant. Stainless steel gearboxes feature IP 65 sealing, Viton shaft seals at the input and output shafts, and a Buna o-ring between the housings. Stainless steel gearboxes also eliminate flat surfaces and allow for a cylindrical design.
Stainless steel gearboxes are more durable than traditional cast iron or epoxy-painted gearboxes. These gearboxes can withstand repeated washdown operations without damage. They also do not collect particles or bacteria. And because stainless steel does not corrode, stainless steel gearboxes can withstand harsh environments, such as oily or greasy environments. Because stainless steel gearboxes are corrosion-resistant, they require little maintenance. They are also easier to clean and maintain, resulting in fewer replacements and a longer life span for your gearbox.
Stainless steel gearboxes are a great choice for food and other industries that require high hygiene standards. In addition to its durability, stainless steel gearboxes are ideal for applications in environments that require high levels of humidity and water. They are also life-lubricated, and they can be supplied with food-grade oils or water. The CZPT Gears stainless gearbox is a versatile option for a variety of applications.
Stainless steel gearboxes offer superior corrosion protection and can withstand harsh environments. The stainless steel cover, housing, and external hardware ensure superior corrosion protection. If you have questions about the varying benefits of stainless steel gearboxes, contact a CZPT Gear sales representative to learn more about your options. And if you are not sure which type is right for your needs, contact a CZPT Gear sales representative to find the perfect solution for your business.
1 speed gearbox
Volkswagen Group Components manufactures the one speed gearbox. The gearbox has a high-performance electric drive motor that produces 310 Nm of torque over a wide speed range. Designed for maximum range, this gearbox uses a single gear for all driving situations. It is extremely quiet, too, and requires precision manufacturing. Volkswagen has also made it available in a reverse-gear configuration with power electronics. Volkswagen’s ID.3 EV’s e-drive motor is a perfect example of this.
The first part of the transmission corresponds to the even and odd gears, while the second part has the straighter gears. A single gear set can change between both modes. An intermediate gear set is also possible. A lastshelf gear can be formed by hydraulically betigte Lamellenkupplungen. Both types of gears can be exchanged between partial transmissions. The invention may furthermore include a transmission with the same gear ratios as the first part of the transmission.
Another variation of the one speed gearbox is the CVT. This type of gearbox has only one drive unit, which means it does not require a clutch or brake. Its power is derived from the torque generated by the Internal Combustion Engine at a particular speed. The engine cannot sustain such high torque levels above 5500 RPM, which will reduce the MPG. Also, raising the RPM will reduce the acceleration, and in severe cases may lead to an engine crash.
As the number of applications for a 1 speed gearbox increases, its design and functionality will continue to evolve. Bosch Rexroth has developed its eGFZ gearbox based on customer feedback. They are currently working on various pilot projects and hope to put it into production in the next few years. However, if you want to buy a 1 speed gearbox now, consider the benefits of a first-rate design.


editor by czh 2022-11-24
China Transmission Geared Motor Unit Screw Drive Lifts Stepper Cyclo Cycloidal Extruder Helical Planetary Bevel Worm Speed Variator Gear Reducer Gearbox wholesaler
Product Description
SRC HELICAL GEARBOX
Products Description
We produce speed reducers in strict accordance with ISO9001 standard to provide our customers with high quality gearboxes at competitive prices. Our gearboxes are equipped with accessories from international famous brands, such as lubricant from Shell brand, and bearing from CZPT brand. The housing and gear are produced in our company under stringent quality control. All our products are available in large stocks, and we can also provide you with customized reducer solutions, pleasefeel confident to contact us.
|
TRC: code for gear units series |
|
1. No code means foot-mounted |
|
2.F: B5 flange mounted |
|
3.Z:B14 flange mounted |
|
Specification code of gear units 01,02.03.04 |
|
B01,MO1……means foot code,without flange |
|
1.I.II1.B5 Output flange specification, defaultl not to write out is ok |
|
2. IECinput flange |
|
3.HS: Shaft input |
|
Transmission ratio of gear units |
|
1.M1: Mounting positio, default mounting position M1 not to write out is ok |
|
1.No mark means without motor |
|
2. Model motos (poles of power)voltage – frequency |
|
voltage – frequency |
|
|
|
|
HangZhou Sihai Machinery Co., Ltd.
History: More than 20 years of experience in the manufacture of reducer products.Scale: Cover working area of 13300 square. meters,have more than 113 employees.
Technology: A group of professional . technical engineers and a strong R&D team.
Management: Scientific ERP management and strict quality control system.
Equipment: 50 CNC lathes,6 machining. centers, 6 gear grinding machines, 2 high-speed.hard hobbing machines, 12 gear hobbing
machines. 10 CNC cylindrical grinding machines,4 CNC internal grinding machines 1spectrometer, high-speed gear shaping 1 machine,
2 gear measuring centers 1 coordinate measuring instrument.
lnnovation: Continuously diversify products range to satisfy customers’needs.Production capacity: 1000 pcs/day.
Long-term supplier of world-class companies: t he main markets are in Southea st Asia, Europe, Middle East.
Marketing model: All export business.
| To Be Negotiated | 1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Type: | Gear Reducer |
| Transport Package: | 1PCS/1box |
| Specification: | aluminium |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
|
TRC: code for gear units series
|
|
1. No code means foot-mounted
|
|
2.F: B5 flange mounted
|
|
3.Z:B14 flange mounted
|
|
Specification code of gear units 01,02.03.04
|
|
B01,MO1……means foot code,without flange
|
|
1.I.II1.B5 Output flange specification, defaultl not to write out is ok
|
|
2. IECinput flange
|
|
3.HS: Shaft input
|
|
Transmission ratio of gear units
|
|
1.M1: Mounting positio, default mounting position M1 not to write out is ok
|
|
1.No mark means without motor
|
|
2. Model motos (poles of power)voltage – frequency
|
|
voltage – frequency
|
|
|
|
|
| To Be Negotiated | 1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Type: | Gear Reducer |
| Transport Package: | 1PCS/1box |
| Specification: | aluminium |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
|
TRC: code for gear units series
|
|
1. No code means foot-mounted
|
|
2.F: B5 flange mounted
|
|
3.Z:B14 flange mounted
|
|
Specification code of gear units 01,02.03.04
|
|
B01,MO1……means foot code,without flange
|
|
1.I.II1.B5 Output flange specification, defaultl not to write out is ok
|
|
2. IECinput flange
|
|
3.HS: Shaft input
|
|
Transmission ratio of gear units
|
|
1.M1: Mounting positio, default mounting position M1 not to write out is ok
|
|
1.No mark means without motor
|
|
2. Model motos (poles of power)voltage – frequency
|
|
voltage – frequency
|
|
|
|
|
Choosing a Gearbox For Your Application
The gearbox is an essential part of bicycles. It is used for several purposes, including speed and force. A gearbox is used to achieve one or both of these goals, but there is always a trade-off. Increasing speed increases wheel speed and forces on the wheels. Similarly, increasing pedal force increases the force on the wheels. This makes it easier for cyclists to accelerate their bicycles. However, this compromise makes the gearbox less efficient than an ideal one.
Dimensions
Gearboxes come in different sizes, so the size of your unit depends on the number of stages. Using a chart to determine how many stages are required will help you determine the dimensions of your unit. The ratios of individual stages are normally greater at the top and get smaller as you get closer to the last reduction. This information is important when choosing the right gearbox for your application. However, the dimensions of your gearbox do not have to be exact. Some manufacturers have guides that outline the required dimensions.
The service factor of a gearbox is a combination of the required reliability, the actual service condition, and the load that the gearbox will endure. It can range from 1.0 to 1.4. If the service factor of a gearbox is 1.0, it means that the unit has just enough capacity to meet your needs, but any extra requirements could cause the unit to fail or overheat. However, service factors of 1.4 are generally sufficient for most industrial applications, since they indicate that a gearbox can withstand 1.4 times its application requirement.
Different sizes also have different shapes. Some types are concentric, while others are parallel or at a right angle. The fourth type of gearbox is called shaft mount and is used when mounting the gearbox by foot is impossible. We will discuss the different mounting positions later. In the meantime, keep these dimensions in mind when choosing a gearbox for your application. If you have space constraints, a concentric gearbox is usually your best option.
Construction
The design and construction of a gearbox entails the integration of various components into a single structure. The components of a gearbox must have sufficient rigidity and adequate vibration damping properties. The design guidelines note the approximate values for the components and recommend the production method. Empirical formulas were used to determine the dimensions of the various components. It was found that these methods can simplify the design process. These methods are also used to calculate the angular and axial displacements of the components of the gearbox.
In this project, we used a 3D modeling software called SOLIDWORKS to create a 3-D model of a gear reducer. We used this software to simulate the structure of the gearbox, and it has powerful design automation tools. Although the gear reducer and housing are separate parts, we model them as a single body. To save time, we also removed the auxiliary elements, such as oil inlets and oil level indicators, from the 3D model.
Our method is based on parameter-optimized deep neural networks (DBNs). This model has both supervised and unsupervised learning capabilities, allowing it to be self-adaptive. This method is superior to traditional methods, which have poor self-adaptive feature extraction and shallow network generalization. Our algorithm is able to recognize faults in different states of the gearbox using its vibration signal. We have tested our model on two gearboxes.
With the help of advanced material science technologies, we can now manufacture the housing for the gearbox using high-quality steel and aluminium alloys. In addition, advanced telematics systems have increased the response time of manufacturers. These technologies are expected to create tremendous opportunities in the coming years and fuel the growth of the gearbox housing market. There are many different ways to construct a gearbox, and these techniques are highly customizable. In this study, we will consider the design and construction of various gearbox types, as well as their components.
Working
A gearbox is a mechanical device that transmits power from one gear to another. The different types of gears are called planetary gears and are used in a variety of applications. Depending on the type of gearbox, it may be concentric, parallel, or at a right angle. The fourth type of gearbox is a shaft mount. The shaft mount type is used in applications that cannot be mounted by foot. The various mounting positions will be discussed later.
Many design guidelines recommend a service factor of 1.0, which needs to be adjusted based on actual service conditions. This factor is the combined measure of external load, required reliability, and overall gearbox life. In general, published service factors are the minimum requirements for a particular application, but a higher value is necessary for severe loading. This calculation is also recommended for high-speed gearboxes. However, the service factor should not be a sole determining factor in the selection process.
The second gear of a pair of gears has more teeth than the first gear. It also turns slower, but with greater torque. The second gear always turns in the opposite direction. The animation demonstrates this change in direction. A gearbox can also have more than one pair of gears, and a first gear may be used for the reverse. When a gear is shifted from one position to another, the second gear is engaged and the first gear is engaged again.
Another term used to describe a gearbox is “gear box.” This term is an interchangeable term for different mechanical units containing gears. Gearboxes are commonly used to alter speed and torque in various applications. Hence, understanding the gearbox and its parts is essential to maintaining your car’s performance. If you want to extend the life of your vehicle, be sure to check the gearbox’s efficiency. The better its functioning, the less likely it is to fail.
Advantages
Automatic transmission boxes are almost identical to mechanical transmission boxes, but they also have an electronic component that determines the comfort of the driver. Automatic transmission boxes use special blocks to manage shifts effectively and take into account information from other systems, as well as the driver’s input. This ensures accuracy and positioning. The following are a few gearbox advantages:
A gearbox creates a small amount of drag when pedaling, but this drag is offset by the increased effort to climb. The external derailleur system is more efficient when adjusted for friction, but it does not create as little drag in dry conditions. The internal gearbox allows engineers to tune the shifting system to minimize braking issues, pedal kickback, and chain growth. As a result, an internal gearbox is a great choice for bikes with high-performance components.
Helical gearboxes offer some advantages, including a low noise level and lower vibration. They are also highly durable and reliable. They can be extended in modular fashion, which makes them more expensive. Gearboxes are best for applications involving heavy loads. Alternatively, you can opt for a gearbox with multiple teeth. A helical gearbox is more durable and robust, but it is also more expensive. However, the benefits far outweigh the disadvantages.
A gearbox with a manual transmission is often more energy-efficient than one with an automatic transmission. Moreover, these cars typically have lower fuel consumption and higher emissions than their automatic counterparts. In addition, the driver does not have to worry about the brakes wearing out quickly. Another advantage of a manual transmission is its affordability. A manual transmission is often available at a lower cost than its automatic counterpart, and repairs and interventions are easier and less costly. And if you have a mechanical problem with the gearbox, you can control the fuel consumption of your vehicle with appropriate driving habits.
Application
While choosing a gearbox for a specific application, the customer should consider the load on the output shaft. High impact loads will wear out gear teeth and shaft bearings, requiring higher service factors. Other factors to consider are the size and style of the output shaft and the environment. Detailed information on these factors will help the customer choose the best gearbox. Several sizing programs are available to determine the most appropriate gearbox for a specific application.
The sizing of a gearbox depends on its input speed, torque, and the motor shaft diameter. The input speed must not exceed the required gearbox’s rating, as high speeds can cause premature seal wear. A low-backlash gearbox may be sufficient for a particular application. Using an output mechanism of the correct size may help increase the input speed. However, this is not recommended for all applications. To choose the right gearbox, check the manufacturer’s warranty and contact customer service representatives.
Different gearboxes have different strengths and weaknesses. A standard gearbox should be durable and flexible, but it must also be able to transfer torque efficiently. There are various types of gears, including open gearing, helical gears, and spur gears. Some of the types of gears can be used to power large industrial machines. For example, the most popular type of gearbox is the planetary drive gearbox. These are used in material handling equipment, conveyor systems, power plants, plastics, and mining. Gearboxes can be used for high-speed applications, such as conveyors, crushers, and moving monorail systems.
Service factors determine the life of a gearbox. Often, manufacturers recommend a service factor of 1.0. However, the actual value may be higher or lower than that. It is often useful to consider the service factor when choosing a gearbox for a particular application. A service factor of 1.4 means that the gearbox can handle 1.4 times the load required. For example, a 1,000-inch-pound gearbox would need a 1,400-inch-pound gearbox. Service factors can be adjusted to suit different applications and conditions.


editor by czh